Lyme disease cause,symptoms, treatments, and medication
Lyme disease, or Lyme borreliosis, is the most commonly transmitted tick-borne infection in the United States and among the most frequently diagnosed tick-borne infections worldwide. Lyme disease is divided into 3 stages: early localized, early disseminated, and late.
Lyme Disease Symptoms
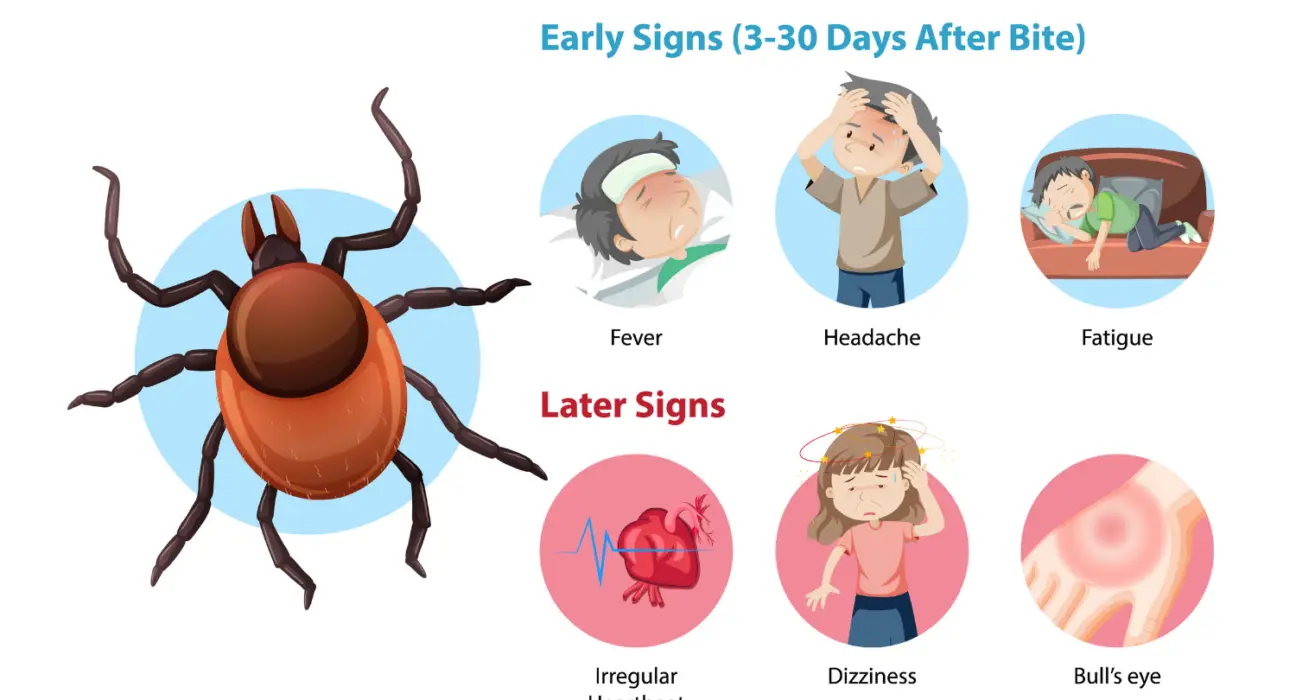
Early symptoms may include fever, chills, headache, fatigue, muscle and joint aches, and swollen lymph nodes. A characteristic rash, often resembling a “bull’s-eye,” can also develop around the tick bite.
Stages:
- Early Localized: Occurs within days to weeks after a tick bite. The characteristic rash and flu-like symptoms may appear.
- Early Disseminated: If untreated, the infection can spread to other parts of the body, leading to more severe symptoms like additional rashes, joint pain, and neurological issues.
- Late Disseminated: Months to years after the initial infection, some people may experience arthritis, neurological problems, or heart issues.
Lyme Disease Treatments
Diagnosis: Lyme disease is diagnosed based on symptoms, physical findings (like the rash), and the history of potential tick exposure. Blood tests can confirm the diagnosis, although they may not be reliable in the early stages.
Treatment: Early-stage Lyme disease is usually treated effectively with antibiotics. Most people recover fully with appropriate treatment, but some may experience lingering symptoms, a condition often referred to as Post-Treatment Lyme Disease Syndrome (PTLDS).





